文件基本概念
文件:指的是音频,图片,视频等等
文件在程序中是以流的形式来操作的
流:数据在数据源(文件)和程序(内存)之间经历的路径
输入流:数据从数据源(文件)到程序(内存)的路径
输出流:数据从程序(内存)到数据源(文件)的路径
创建文件
方式一:
public class FileCreate {
public static void main(String[] args) {
}
//创建文件方式一:new File(String FilePath)
@Test
public void Create01() throws IOException {
String FilePath = "/Users/Desktop/createPath01.txt";
File file = new File(FilePath);
file.createNewFile();
System.out.println("文件创建成功");
}
}

方式二:
public class FileCreate {
public static void main(String[] args) {
}
//方式二: new File(File parent,String child)
@Test
public void Create02() throws IOException {
File Parentfile = new File("/Users/Desktop");
String chileFile = "createPath02.txt";
File file = new File(Parentfile, chileFile);
file.createNewFile();
}
}

细节:
放你创建new File()得到的file文件的时候,其实知识在内存中有一个file而已,只是一个java对象而已,并没有到硬盘中,当你使用方法createNewFile()方法时,它才真正写入了磁盘中
第一个方法是直接指定路径创建文件,第二种是根据已知文件名创建新文件在那已知文件目录上,第三种是通过路径,通过已知旧文件路径创建
方式三:
public class FileCreate {
public static void main(String[] args) {
}
//方式三:父目录+子目录构建 new File(String parent,String chile)
@Test
public void Create03() throws IOException {
String parent = "/Users/Desktop";
String chile = "createPath03.txt";
File file = new File(parent, chile);
file.createNewFile();
}
}

常用文件操作
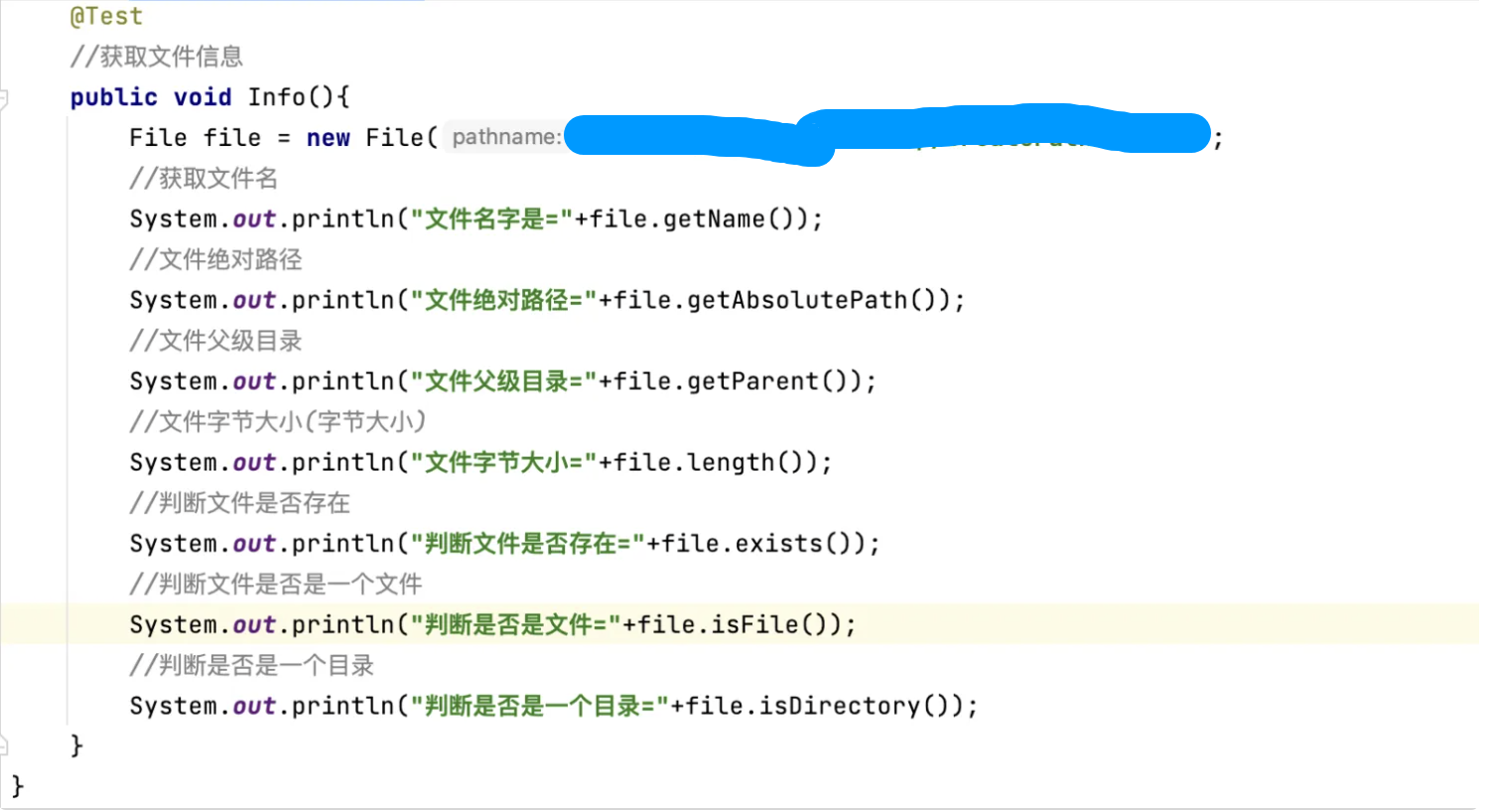
获取文件名字,获取文件绝对路径 ,文件父级目录,文件大小(按照字节数来算的),判断文件是否存在,判断是否是文件,判断是否是目录
在utf-8的情况下,一个汉字三个字节,一个字母一个字节
目录操作
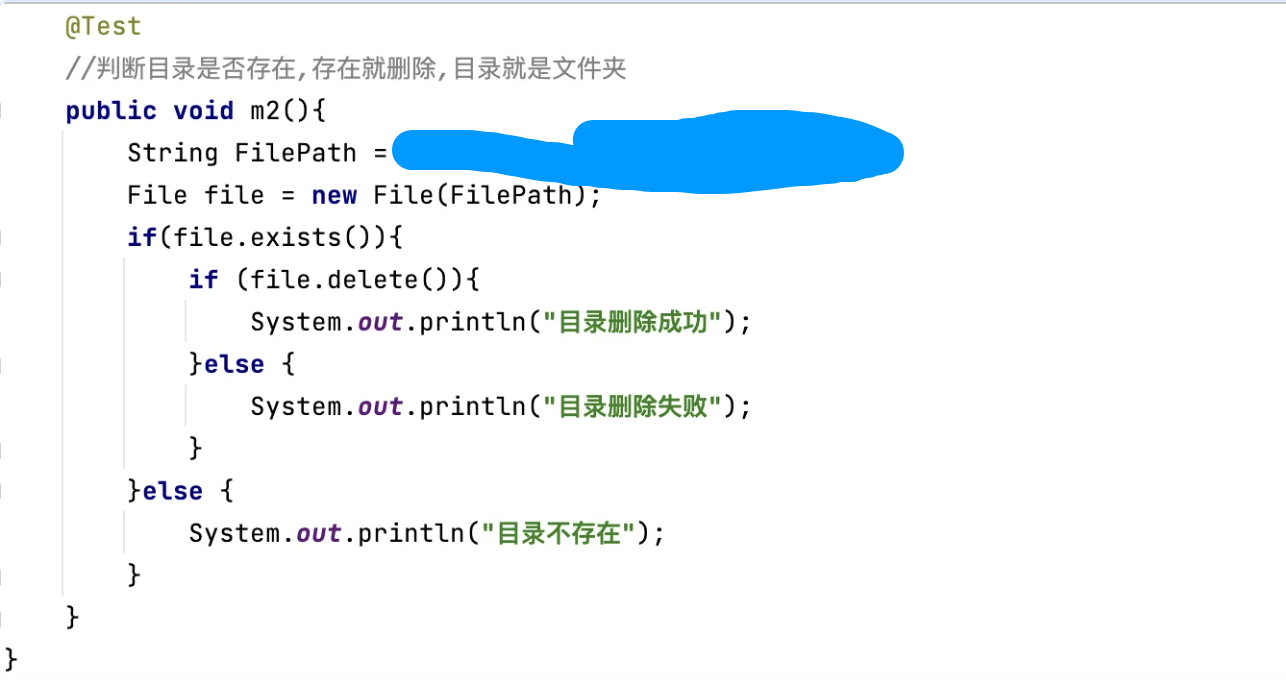
删除操作


删除目录,目录就是文件夹

创建目录
mkdirs:创建多级目录


io流原理和分类
1.I/O是Input/Output的缩写,I/O技术是非常实用的技术,用于处理数据传输,如读写文件,网络通讯等
2.Java程序中,对于数据的输入/输出操作以"流(stream)"的方式进行
3.java.io包下提供了各种"流"类和接口,用于以获取不同种类的数据,并通过方法输入或者输出数据
4.输入input:读取外部数据(磁盘,光盘等存储设备的数据)到程序(内存中)
5.输出output:将程序(内存)数据输出到硬盘,光盘等存储设备中
InputStream
FileInputStream
read方法
字节输入流,将文件读取到程序中
1.read()方法
这里只能读字符,如果有汉字,就会乱码,因为read是一个字节一个字节读的,但是一个汉字是三个字节
import org.testng.annotations.Test;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class FileInputStream_ {
public static void main(String[] args) {
}
@Test
/**
* 用read()方法来读取文件,字节输入流,read无参构造,在官方文档中,当读到-1的时候,就是读完了
* */
public void Fileread01(){
String FilePath = "/Users/Desktop/p.txt";
FileInputStream fileInputStream = null;
int readnum = 0;
try {
fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(FilePath);
while ((readnum = fileInputStream.read())!=-1){
System.out.print((char)readnum);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
try {
fileInputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
}
2.read(byte[] b)
import org.testng.annotations.Test;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class FileInputStream_ {
public static void main(String[] args) {
}
@Test
/**
* 用read(byte[] b)方法来读取文件,字节输入流,read数组读取,在官方文档中,当读到-1的时候,就是读完了
* */
public void Fileread02(){
String FilePath = "/Users/Desktop/p.txt";
FileInputStream fileInputStream = null;
int readlength = 0;
byte[] by = new byte[8];
try {
fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(FilePath);
while ((readlength = fileInputStream.read(by))!=-1){
System.out.print(new String(by,0,readlength));
}
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
try {
fileInputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
}OutputStream
FileOutputStream
字节输出流
第一种方式
@Test
public void OutputFile01(){
String FilePath = "/Users/Desktop/b.txt";
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = null;
try {
fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(FilePath);
fileOutputStream.write('a');
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
try {
fileOutputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}第二种方式
@Test
public void OutputFile02(){
String FilePath = "/Users/Desktop/b.txt";
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = null;
String str = "abcdefg";
try {
fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(FilePath);
fileOutputStream.write(str.getBytes());
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
try {
fileOutputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}第三种
@Test
public void OutputFile02(){
String FilePath = "/Users/Desktop/b.txt";
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = null;
String str = "abcdefg";
try {
fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(FilePath);
fileOutputStream.write(str.getBytes(),0,3);
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
try {
fileOutputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}如果不希望覆盖就加true
@Test
public void OutputFile02(){
String FilePath = "/Users/Desktop/b.txt";
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = null;
String str = "abcdefg";
try {
fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(FilePath,true);
fileOutputStream.write(str.getBytes(),0,3);
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
try {
fileOutputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}文件拷贝
这里的思路就是:
将要拷贝的文件通过输入流读到程序中,之后,在通过输出流将程序的数据输出到指定路径的文件,就是一个文件拷贝的流程,这里面文件传输过程中是读一些拷贝一些,以为如果文件太大,不容易成功,所以必须循环
而且必须使用write(buf,0,strlen)这个形式,如果不加0,strlen,那么文件可能会错误,因为如果你的文件是1025,但是它大小是1024,那么就会丢失数据
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class FileCopy_ {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String Apath = "/Users/Desktop/b.txt";
String Bpath = "/Users/Desktop/b02.txt";
FileInputStream fileInputStream = null;
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = null;
byte[] buf = new byte[1024];
int strlen = 0;
try {
fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(Apath);
fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(Bpath);
while ((strlen =fileInputStream.read(buf))!=-1){
fileOutputStream.write(buf,0,strlen);
}
System.out.println("文件拷贝成功");
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
try {
if(fileInputStream!=null){
fileInputStream.close();
}
if (fileOutputStream!=null){
fileOutputStream.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
}
FileReader
字符输入流
read方法单个字符一个一个读取
@Test
//单个字符读入read
public void Filereader01(){
String filePath = "/Users/Desktop/b.txt";
FileReader fileReader = null;
int ch = 0;
try {
fileReader = new FileReader(filePath);
while ((ch = fileReader.read())!=-1){
System.out.print((char)ch);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
if(fileReader!=null){
try {
fileReader.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
}read读取字符数组形式
@Test
//read使用字符数组的形式读取
public void FileReader02(){
String filePath = "/Users/Desktop/b.txt";
FileReader fileReader = null;
int len = 0;
char[] ch = new char[8];
try {
fileReader = new FileReader(filePath);
while ((len = fileReader.read(ch))!=-1){
System.out.print(new String(ch,0,len));
}
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
if(fileReader!=null){
try {
fileReader.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
}FileWriter
字符输出流
public class FileWriter_ {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String filePath = "/Users/Desktop/aa.txt";
FileWriter fileWriter = null;
char[] ch = {'a','b','c','d'};
try {
fileWriter = new FileWriter(filePath);
//写入单个字符
fileWriter.write('T');
//写入指定数组
fileWriter.write(ch);
//写入指定数组的指定部分
fileWriter.write("123456".toCharArray(),0,2);
//写入整个字符串
fileWriter.write("zxc");
//写入字符串的指定部分
fileWriter.write("qwert",0,2);
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
if(fileWriter!=null){
try {
fileWriter.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
}
}
细节(很重要)
在使用FileWriter的时候,必须关闭流,否则数据进不去
BufferedReader
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.FileReader;
public class BufferedReader_ {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
String filePath = "/Users/Desktop/b.txt";
BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(filePath));
String line;
while((line = bufferedReader.readLine())!=null){
System.out.println(line);
}
bufferedReader.close();
}
}
使用处理流一定要关闭资源,关闭处理流的资源就可以,会自动关闭节点流的
BufferedWriter
import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
public class BufferedWriter_ {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String filePath = "/Users/abc.txt";
BufferedWriter bufferedWriter = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(filePath,true));
bufferedWriter.write("hello,你好");
bufferedWriter.newLine();//换行符
bufferedWriter.write("hello,你好");
bufferedWriter.close();
}
}
使用处理流一定要关闭资源,关闭处理流的资源就可以,会自动关闭节点流的
缓冲流文件拷贝
import java.io.*;
public class BufferedCopy_ {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String filepath01 = "/Users/Desktop/p.txt";
String filepath02 = "/Users/Desktop/p1.txt";
BufferedReader br = null;
BufferedWriter bw = null;
String line;
try {
br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(filepath01));
bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(filepath02));
while((line = br.readLine())!=null){
bw.write(line);
bw.newLine();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
try {
if(br!=null){
br.close();
}
if(bw!=null){
bw.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
}
细节
BufferedReader和BufferWriter都是字符文件,所以不要读取二进制文件(声音,视频word文档,pdf文档)
BufferedInputStream和BufferedOutputStream
既可以处理二进制文件又可以处理文本文件
import java.io.*;
public class BufferedCopy02_ {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String filePath01 = "/Users/Desktop/1.png";
String filePath02 = "/Users/Desktop/2.png";
BufferedInputStream bi = null;
BufferedOutputStream bo = null;
byte[] buff = new byte[1024];
int len = 0;
try {
bi = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(filePath01));
bo = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(filePath02));
while((len = bi.read(buff))!=-1){
bo.write(buff,0,len);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
try {
if(bi!=null){
bi.close();
}
if(bo!=null){
bo.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
}
ObjectOutputStream
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
import java.io.Serializable;
public class ObjectOutputStream_ {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//序列化后,保存的文件格式,不是存文本,而是按照他的格式来保存
String filePath = "/Users/Desktop/zx1.dat";
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(filePath));
//序列化数据到/Users/tanbowen/Desktop/zx1.dat
oos.writeInt(100);//int->Integer(实现了Serializable)
oos.writeBoolean(true);//boolean->Boolean(实现了Serializable)
oos.writeChar('a');//char->character(实现了Serializable)
oos.writeDouble(9.5);//double->Double(实现了Serializable)
oos.writeUTF("哈尔滨学院");//String(实现了Serializable)
oos.writeObject(new dog("旺财",10));//因为dog实现了Serializable
}
}
class dog implements Serializable {
private String name;
private int age;
public dog(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
}
ObjectInputStream
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
public class ObjectFileInputStream_ {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
String filePath = "/Users/Desktop/zx1.dat";
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(filePath));
System.out.println(ois.readInt());
System.out.println(ois.readBoolean());
System.out.println(ois.readChar());
System.out.println(ois.readDouble());
System.out.println(ois.readUTF());
System.out.println(ois.readObject());
ois.close();
}
}
打印流(只有输出流,没有输入流)
字节打印流
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintStream;
public class PrintStream_ {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//字节打印流
PrintStream out = System.out;
out.println("string");
//print底层就是write
out.write("string".getBytes());
out.close();
//修改输出位置
System.setOut(new PrintStream("/Users/Desktop/zxc.txt"));
System.out.println("hello,小花");
}
}
字符打印流
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
public class PrintWrite_ {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
PrintWriter printWriter = new PrintWriter(new FileWriter("/Users/Desktop/vb.txt"));
printWriter.print("hi");
printWriter.close();
}
}这个close必须写,如果不写,数据就不会写到文件里面
Properties
读取properties文件(传统方法)
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
public class readproperties_ {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("src/file.properties"));
String line = "";
while((line = bufferedReader.readLine())!=null){
String[] split = line.split("=");
System.out.println(split[0]+":"+split[1]);
}
bufferedReader.close();
}
}
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Properties;
public class Properties_ {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//用Properties读取
Properties properties = new Properties();
//获取资源路径
properties.load(new FileReader("src/file.properties"));
//重定向位置
properties.list(System.out);
String user = properties.getProperty("user");
String psw = properties.getProperty("psw");
System.out.println(user);
System.out.println(psw);
}
}
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Properties;
public class Properties_ {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Properties properties = new Properties();
//创建
properties.setProperty("user","abc");
properties.setProperty("psw","123");
//配置
properties.store(new FileOutputStream("src/file02.properties"),null);
System.out.println("文件配置成功");
}
}
这里如果保存的是中文,那么在文件里面显示的是unicode码
setProperty没有k就创建,有k就修改